All About The Critical Illness Insurance Policy & The Benefits of Critical Illness Insurance
By Canadian LIC, October 19, 2023, 8 Minutes
- All About The Critical Illness Insurance Policy & The Benefits of Critical Illness Insurance
- About Critical Illness Insurance
- How Does Critical Illness Insurance Work in Canada?
- Is it worth buying critical illness insurance in Canada?
- Does my health insurance cover critical illnesses?
- How much critical illness insurance do I need?
- When to buy Critical Illness Insurance?
- Benefits of Critical Illness Insurance
- In Conclusion
A form of financial protection called critical illness insurance was created to shield Canadians from the heavy financial constraints that can result from being diagnosed with a life-threatening illness. The aim, operation, typical coverage, and advantages offered to policyholders of critical illness insurance in Canada will all be covered in detail here.
About Critical Illness Insurance
When a covered critical illness is diagnosed, a particular kind of insurance coverage called Critical Illness Insurance pays the policyholder a lump sum. This payment is made tax-free and is available for use at the policyholder’s choice, providing financial flexibility during a trying period. With a focus on providing financial support when a major sickness is detected, Critical Illness Insurance differs from standard health insurance, which covers medical costs.
Read More – Critical Illness Insurance here
How Does Critical Illness Insurance Work in Canada?
Critical Illness Insurance works on a very simple premise:
- Purchase a Policy: Individuals in Canada can purchase a Critical Illness Insurance policy from an insurance provider. The policyholder pays regular premiums, typically monthly or annually, to maintain coverage.
- Diagnosis of a Covered Illness: If the policyholder is diagnosed with a critical illness covered by the policy, they become eligible to make a claim.
- Claim Submission: The policyholder or their designated beneficiary submits a claim to the insurance provider. This claim includes medical documentation confirming the diagnosis of the covered critical illness.
- Claim Evaluation: The insurance provider reviews the claim to ensure it meets the policy’s criteria for the specific critical illness. If the claim is approved, a lump-sum payment is made to the policyholder.
- Lump-Sum Payout: Upon approval, the policyholder receives a tax-free lump-sum payment. This payment can be used for any purpose, such as covering medical expenses, paying off debts, maintaining their standard of living, or pursuing alternative treatments.
Is it worth buying critical illness insurance in Canada?
The decision to purchase Critical Illness Insurance in Canada, as in any other country, is a highly individual one and depends on your specific circumstances, needs, and priorities. It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution, and what may be a valuable investment for one person may not be the same for another. Here are some factors to consider when determining if Critical Illness Insurance is worth buying in Canada:
- Current Financial Situation: Evaluate your current financial situation, including savings, investments, and other insurance coverage. Suppose you have substantial financial resources that can comfortably cover medical expenses and maintain your lifestyle in the event of a critical illness. In that case, you may have less need for Critical Illness Insurance. However, if a significant financial burden arises from such an illness, insurance can provide valuable protection.
- Health and Family History: Consider your personal health history and your family’s medical history. If you have a family history of specific critical illnesses or if you have lifestyle factors that put you at higher risk (e.g., smoking, sedentary lifestyle), having Critical Illness Insurance may be more important to you.
- Existing Insurance Coverage: Review your existing insurance coverage, including health insurance and disability insurance. While these policies provide certain protections, they may not cover all the financial challenges associated with a critical illness, such as non-medical expenses or experimental treatments. Critical Illness Insurance can complement these policies by providing additional coverage.
- Debt and Financial Obligations: Consider your financial commitments, such as mortgage payments, student loans, or other debts. Critical Illness Insurance can ensure that these financial obligations are met if you become critically ill and are unable to work. It can provide peace of mind knowing that your debts won’t become a burden to you or your family during recovery.
- Risk Tolerance: Assess your risk tolerance and willingness to take on financial risk. Some individuals prefer to have a financial safety net in place, even if it means paying insurance premiums. The knowledge that they have protection in case of a critical illness outweighs the cost of the premiums.
- Affordability: Determine if the premiums for Critical Illness Insurance fit within your budget. It’s essential to strike a balance between coverage and affordability. Work with an insurance advisor to find a policy that aligns with your financial situation.
- Family and Dependents: If you have dependents or a family that relies on your income, Critical Illness Insurance can provide significant benefits. It ensures that your family’s financial needs are met and that they can maintain their standard of living during your recovery.
- Personal Peace of Mind: Beyond the financial considerations, think about your peace of mind. Some people value knowing that they have financial protection in place for unforeseen circumstances. This emotional security can be an essential aspect of Critical Illness Insurance. In conclusion, Critical Illness Insurance in Canada can be a valuable investment for individuals who want to protect their financial well-being in the event of a severe medical condition.
Does my health insurance cover critical illnesses?
In Canada, the healthcare system provides universal access to medically necessary hospital and physician services through provincial and territorial health insurance plans. This coverage ensures that Canadians have access to essential medical services without direct out-of-pocket payments at the point of care.
However, it’s important to note that while Canada’s public healthcare system covers a wide range of medical services, including hospital stays and physician visits, it does not provide comprehensive coverage for all aspects of healthcare. In particular, the public healthcare system does not cover certain expenses related to critical illnesses, such as:
- Prescription Drugs: While some provinces have programs that provide drug coverage for specific populations (e.g., seniors and low-income individuals), prescription drug coverage is not universally comprehensive. Many prescription medications used in the treatment of critical illnesses may not be fully covered.
- Medical Equipment and Supplies: Specialized medical equipment and supplies, such as mobility aids or devices required during recovery, may not be covered by the public healthcare system.
- Home Care Services: In some cases, individuals recovering from a critical illness may require home care services, which may not be fully covered or may have limitations under the public system.
- Travel Expenses: If you need to travel for specialized medical treatments or consultations not available locally, the public healthcare system does not typically cover travel expenses.
- Non-Medical Expenses: Critical illnesses can result in non-medical expenses, such as modifications to your home to accommodate your condition, child care, and other related costs. These expenses are generally not covered.
- Lost Income: If you are unable to work due to a critical illness, the public healthcare system does not provide income replacement. This can result in a significant financial burden, especially if you have ongoing financial obligations.
This is where Critical Illness Insurance comes into play. Critical Illness Insurance is a separate insurance policy that provides a lump-sum payment to the policyholder upon the diagnosis of a covered critical illness. The lump-sum payment is tax-free and can be used for various purposes, including covering the expenses and financial challenges associated with a critical illness that is not covered by the public healthcare system.
While Canada’s public healthcare system provides essential medical coverage, it does not provide comprehensive coverage for all aspects of healthcare, especially when it comes to critical illnesses. Critical Illness Insurance is designed to fill these gaps by offering financial protection and flexibility in the face of a life-altering medical condition. It can help you maintain your financial stability and access the best possible care during a challenging time.
How much critical illness insurance do I need?
Determining how much Critical Illness Insurance you need is a personal decision that depends on various factors, including your financial situation, lifestyle, and specific needs. Here are some steps to help you estimate the appropriate coverage amount:
Assess Your Financial Situation:
Start by evaluating your current financial status, including savings, investments, and existing insurance coverage.
Calculate your monthly or annual expenses, including mortgage or rent, utilities, groceries, transportation, and discretionary spending.
Consider any outstanding debts, such as a mortgage, car loans, credit card balances, and student loans.
Identify Your Financial Obligations:
Determine if you have any specific financial obligations or goals, such as funding your children’s education, saving for retirement, or paying off debts.
Assess how a critical illness diagnosis might affect your ability to meet these obligations.
Calculate Medical Expenses:
Estimate potential medical expenses associated with a critical illness, including treatments, medications, medical equipment, and specialized care. Consider expenses not covered by public healthcare or other insurance policies.
Factor in Non-Medical Costs:
Recognize non-medical expenses that may arise during your illness, such as home modifications, travel for specialized treatments, child care, and household help. These expenses can have a significant impact on your financial well-being.
Assess Income Replacement Needs:
Determine whether you would need income replacement if you were unable to work during your illness.Calculate the duration for which you might require this income replacement.
Review Existing Insurance Policies:
Understand the coverage provided by your existing insurance policies, such as disability insurance and life insurance.Determine if these policies would cover some of the financial needs arising from a critical illness.
Consider Family and Dependents:
If you have dependents or a family that relies on your income, consider their financial needs and how they would be affected by your illness.
Factor in Savings and Investments:
Assess how much of your savings and investments you are willing to use to cover expenses during your illness.Decide if you want to preserve these assets for future goals.
Consult with a Financial Advisor:
Consider seeking advice from a financial advisor or insurance professional who can help you assess your specific needs and create a customized plan.
Choose a Coverage Amount:
Based on your assessment, determine the coverage amount that would adequately address your financial needs and provide peace of mind.
Remember that the appropriate coverage amount can vary widely from person to person. It should align with your unique financial goals and risk tolerance. It’s also important to review and adjust your coverage periodically as your financial situation changes, such as when you take on new financial responsibilities, have children, or reach retirement age.
Ultimately, Critical Illness Insurance is designed to provide financial protection and flexibility during a challenging time. The coverage amount you choose should offer peace and help you maintain your financial stability, allowing you to focus on your recovery and well-being in the event of a critical illness.
Get The Best Insurance Quote From Canadian L.I.C
Call 1 844-542-4678 to speak to our advisors.

When to buy Critical Illness Insurance?
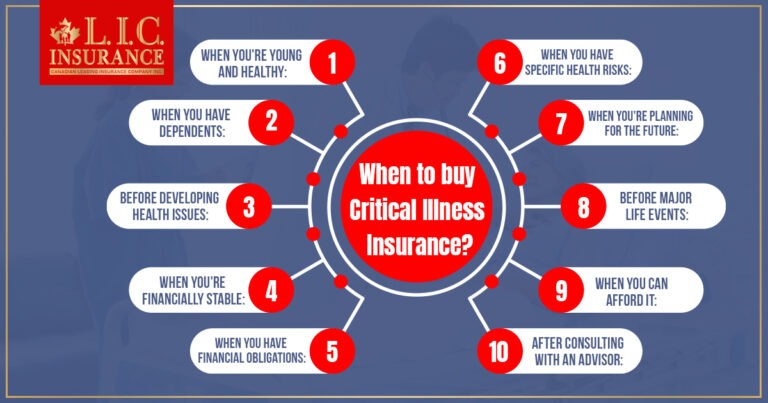
The timing of when to buy Critical Illness Insurance in Canada is an important consideration that can impact your coverage and premiums. Here are some key factors to help you determine when it may be the right time to purchase Critical Illness Insurance:
When You’re Young and Healthy:
One of the most advantageous times to purchase Critical Illness Insurance is when you’re young and in good health. Premiums are typically lower for younger individuals because the risk of developing a critical illness is lower. Buying coverage early can lock in lower premiums for the life of the policy.
When You Have Dependents:
If you have dependents, such as a spouse or children, purchasing Critical Illness Insurance becomes more crucial. It ensures that your family’s financial needs are met in the event of a critical illness diagnosis.
Before Developing Health Issues:
It’s generally easier to obtain Critical Illness Insurance when you’re in good health and haven’t been diagnosed with any pre-existing medical conditions. Some medical conditions may make it more challenging to qualify for coverage or result in higher premiums.
When You’re Financially Stable:
It’s ideal to purchase Critical Illness Insurance when you are financially stable and have the means to pay the premiums. This ensures that you can maintain coverage without financial strain.
When You Have Financial Obligations:
If you have significant financial obligations, such as a mortgage, student loans, or other debts, purchasing Critical Illness Insurance can provide peace of mind that these obligations will be met even if you are unable to work due to a critical illness.
When You Have Specific Health Risks:
If you have a family history of certain critical illnesses or lifestyle factors that put you at higher risk, it may be wise to purchase coverage sooner rather than later. Some insurance policies may exclude coverage for pre-existing conditions, so obtaining coverage before a diagnosis is essential.
When You’re Planning for the Future:
Critical Illness Insurance can be a valuable part of your long-term financial planning. If you have specific financial goals or want to protect your assets and investments, it’s worth considering this type of insurance.
Before Major Life Events:
Significant life events, such as getting married, having children, or buying a home, can be ideal times to assess your insurance needs, including Critical Illness Insurance. These events may increase your financial responsibilities and make insurance coverage more important.
When You Can Afford It:
While it’s essential to purchase insurance when you’re financially stable, you should also consider the affordability of the premiums. Choose a policy that fits within your budget to ensure you can maintain coverage over the long term.
After Consulting with an Advisor:
Consider consulting with a financial advisor or insurance professional who can assess your unique circumstances and recommend the right time to purchase Critical Illness Insurance based on your financial goals and risk tolerance.
The timing of when to buy Critical Illness Insurance in Canada should align with your health, financial situation, and life stage. Purchasing coverage early can provide cost savings and peace of mind, but it’s never too late to consider this insurance if you haven’t already. The most important factor is to make an informed decision based on your individual needs and priorities.
Benefits of Critical Illness Insurance
Critical Illness Insurance in Canada offers several significant benefits that can provide financial security and peace of mind to policyholders. Here are the key advantages of having Critical Illness Insurance:
Read More – Critical Illness Insurance here
- Financial Security During Critical Illness: The primary benefit of Critical Illness Insurance is that it provides a lump-sum payment to the policyholder upon the diagnosis of a covered critical illness. This lump-sum payout is tax-free and can be used at the discretion of the policyholder. It serves as a financial safety net, helping you cover medical expenses, treatments, and other costs associated with a critical illness.
- Flexibility in Use: Unlike some insurance policies with restrictions on how the payout can be used, Critical Illness Insurance offers unparalleled flexibility. You can allocate the funds as needed, whether it’s for medical bills, mortgage or rent payments, household expenses, debt repayment, or pursuing alternative treatments. This flexibility ensures that you have the financial means to address your specific needs during a challenging time.
- Protection for Your Loved Ones: Critical Illness Insurance doesn’t just protect you; it safeguards the financial well-being of your loved ones. The lump-sum payment ensures that your family doesn’t bear the financial burden while they support you through your recovery. In the unfortunate event of your passing, the payout can serve as a financial legacy for your beneficiaries.
- Coverage Gaps in Traditional Health Insurance: While Canada’s healthcare system is comprehensive, there can still be significant gaps in coverage, especially for certain treatments and medications. Critical Illness Insurance bridges these gaps by providing financial support that isn’t limited to medical expenses. This ensures that you have the means to access the best possible treatments, including experimental or alternative therapies.
- Coverage Beyond Disability Insurance: People often confuse Critical Illness Insurance with Disability Insurance. While both provide financial support in times of health-related challenges, they serve different purposes. Disability Insurance typically provides ongoing income replacement if you are unable to work due to a disability, whereas Critical Illness Insurance provides a lump-sum payment upon the diagnosis of a critical illness, regardless of your ability to work. Having both types of coverage can offer comprehensive protection for your financial future.
- Additional Peace of Mind: Knowing that you have Critical Illness Insurance can bring peace of mind. In a world where health is unpredictable, this coverage offers reassurance that you and your family will be financially secure if the unexpected occurs. It allows you to focus on recovery rather than worrying about medical bills and other financial obligations.
- Coverage for Non-Medical Expenses: Critical Illness Insurance doesn’t just cover medical costs. It can also assist with non-medical expenses that may arise during your illness. These can include travel expenses for specialized treatments, childcare, home modifications to accommodate your condition, or hiring a caregiver to assist with daily tasks.
- Preservation of Financial Assets: Critical Illness Insurance can help protect your savings, investments, and retirement funds from being depleted by medical expenses. It allows you to preserve your financial assets for future goals and needs.
- Customized Coverage: Critical Illness Insurance policies in Canada can be tailored to your specific needs and budget. You can choose the coverage amount and options that align with your individual circumstances.
In Conclusion
Critical Illness Insurance in Canada is a valuable component of a comprehensive financial plan. It offers financial security, flexibility, and peace of mind during times of severe illness. While it may not be necessary for everyone, it is a valuable consideration for those with specific health risks, financial obligations, or a desire for added security. When considering Critical Illness Insurance, consult with a financial advisor like Canadian LIC who can assess your unique circumstances and help you determine if it’s the right choice for you. Having this coverage provides the reassurance that, should the unexpected occur, your health and financial well-being are protected, allowing you to focus on what truly matters—your recovery and your loved ones.
Get The Best Insurance Quote From Canadian L.I.C
Call 1 844-542-4678 to speak to our advisors.
The above information is only meant to be informative. It comes from Canadian LIC’s own opinions, which can change at any time. This material is not meant to be financial or legal advice, and it should not be interpreted as such. If someone decides to act on the information on this page, Canadian LIC is not responsible for what happens. Every attempt is made to provide accurate and up-to-date information on Canadian LIC. Some of the terms, conditions, limitations, exclusions, termination, and other parts of the policies mentioned above may not be included, which may be important to the policy choice. For full details, please refer to the actual policy documents. If there is any disagreement, the language in the actual policy documents will be used. All rights reserved.
Please let us know if there is anything that should be updated, removed, or corrected from this article. Send an email to Contact@canadianlic.com or Info@canadianlic.com


